Eulag
Eulag
All-Scales Geophysical Research Model |



 |
|
below is a set of conditions specific for this test case:
parameter (n=128,m=64,l=51) ! grid dimensions
parameter (dx00=10.)
parameter (dy00=10.)
parameter (dz00=10.)
parameter (dt00=0.25)
parameter (nt=600,noutp=10,nplot=10,nstore=600,nslice=0)
parameter (iwrite=0,iwrite0=0,irst=0)
parameter (nt=1440,noutp=288,nplot=288,nstore=720,nslice=0)
parameter (iwrite=1,iwrite0=0,irst=0)
parameter (icyx=1)
parameter (icyy=0)
parameter (implgw=1,isphere=0,icylind=0,icorio=0)
#define SGS 1 /* 0=NO DIFFUSION, 1=OLD DISSIP, 2=DISSIP AMR */
parameter (icyy=1)
parameter (ivs0=1) ! Viscous/Inviscid model
parameter (itke0=1,itke=ivs0*itke0) ! Smagorinsky/TKE SGS model
parameter (ichm=1,nspc=1) ! chemical spices
parameter (imrsb=1)
ccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccc
create environmental profiles (use subroutine tinit_i) c
c-----------------------------------------------------------------c
c---> u00 - wind constant; x component, profile U (m/s) c
c---> v00 - wind constant; y component, profile V (m/s) c
c---> st - stability parameter; inverse scale height (m^-1) c
c---> u0z - vertical wind shear dU/dz (s^-1) c
c---> v0z - vertical wind shear dV/dz (s^-1) c
ccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccc
data u00, v00, st, u0z, v0z
$ /10.0, 0.0, 1.0e-5, 0.e-3, 0.e-3/
ccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccc
create mountain
c-----------------------------------------------------------------c
c amp - maximum height of mountain [m]
c xml - zonal scale of mountain [m] or [radians]
c xml0 - zonal shift from the domain center [m] or [radians]
c yml - meridional scale of mountain [m] or [radians]
c yml0 - meridional shift from the domain center [m] or [radians]
c angle- angle to skew the mountain ridge [radians]
ccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccccc
common/gora/ xml,yml,amp,xml0,yml0,angle
data amp,xml,yml,xml0,yml0,angle/100.,2*100.,-200.,0.,0./
Following are other case specific setups
C initialization of the passive source of the tracer.
do ispc=1,nspc
do k=1,l
do j=1,mp
do i=1,np
.....
chm(i,j,k,ispc) = 0.
fchm(i,j,k,ispc) = 1000.0
Setup orographical features inside subroutine topolog
rd(xln,ylt)=sqrt(((xln-xml0)/xml)**2+((ylt-yml0)/yml)**2)
rb(xln,ylt)=sqrt(((xln+xml0)/xml)**2+((ylt+yml0)/yml)**2)
rc(xln,ylt)=sqrt(((xln )/xml)**2+((ylt-xml0)/yml)**2)
profm(rad)=.5*(1.+cos(pi*rad))
Setup for the lower topography "zs(n,m)":
xx= cang*(x(ia)-x0)+sang*(y(ja)-y0)
yy=-sang*(x(ia)-x0)+cang*(y(ja)-y0)
rr=rd(xx,yy)
zs(i,j)= 0.
zs(i,j)=amp*cvmgm(0.,profm(rr),1.-rr)
...
Setup for the mmersed boundary object "szib2(n,m)":
gij=zb/(zh(i,j)-zs(i,j)) ! define terrain following transformation
zloc=(k-1)*dz ! compute unstretched uniform height
zcrl=zloc/gij+zs(i,j) ! height in terrain following coordinates
zsib(i,j,k)=-1. ! default, no IMB points
xx= cang*(x(ia)-x0)+sang*(y(ja)-y0)
yy=-sang*(x(ia)-x0)+cang*(y(ja)-y0)
if(itopo.eq.0) rrb=rb(xx,yy) ! object shifted in X
if(itopo.eq.1) rrb=rc(xx,yy) ! object shifted in Y
zsib2(i,j)=amp*cvmgm(0.,1.,1.-rrb)
if(zcrl.lt.zsib2(i,j)) then ! check if grid height below object
zsib(i,j,k)=1. ! add IMB points below zsib2 surface
endif
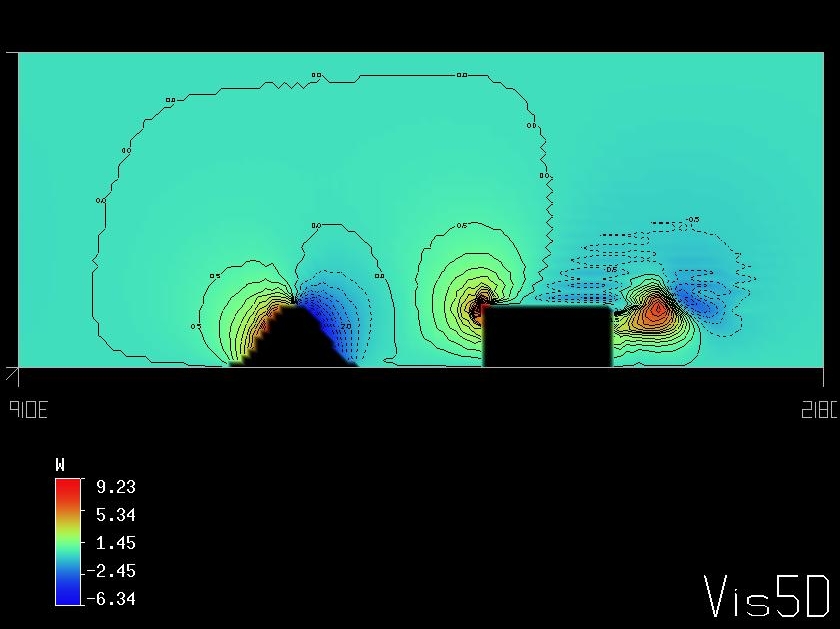
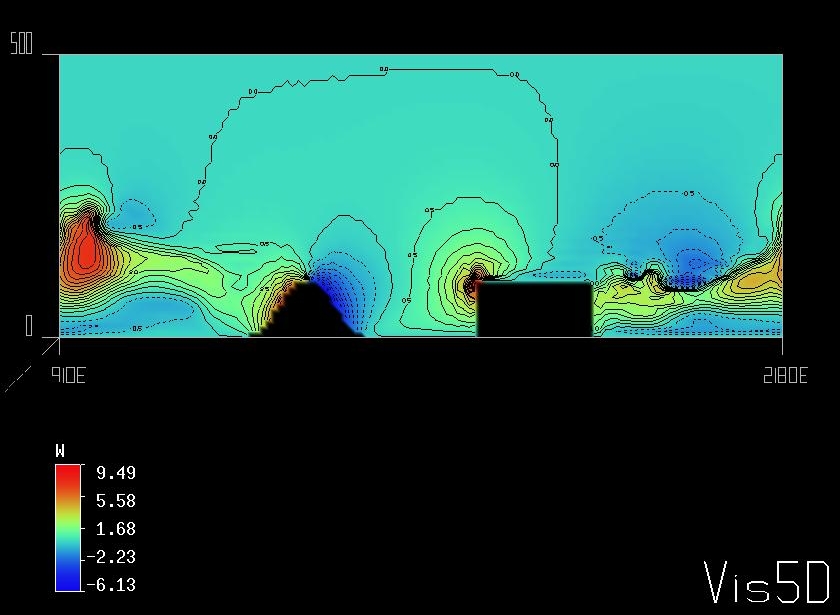
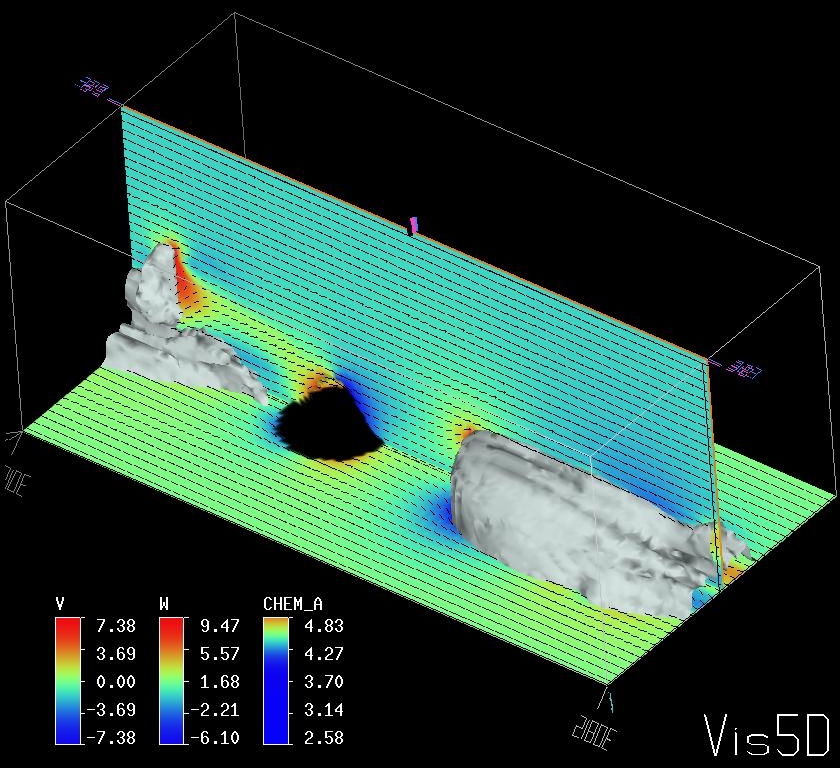
Figure 1 snd Figure 2 shows the vertical velocity fields after t=8 sec and t=30 sec respectively. The cross sections of the U, W velocity components and the isosurface of the passive tracer are presented at Figure 3. |