
NMC Office Note 29 can be found at:
See examples in the appendices of the RAWINS/DATAGRID Tech Note.
KBOGUS: Change Existing Observations.
NBOGUS: Insert Station Reports.
NSELIM: Remove Station Reports.
AUTOGBOGUS: Subjective Examination of Suspect Data
Submit |
0 = Not an Autobogus submittal. |
InObs |
ARCHIVE = use
archived NMC observations. |
SFCsw |
Flag to indicate whether surface observations are to be accessed ( SFCsw = SFC , recommended) or not ( SFCsw = NoSFC ). |
BOGUSsw |
Flag to indicate the type of bogus data to be used: NoBOG : Not a bogus job. |
InDatg |
Pathname for the REGRID output used as input to RAWINS . |
InRaobs |
Pathname for the RAOB data (see ~mesouser/catalog/catalog.raob file; for pre-1984 cases, see ~mesouser/catalog/catalog.raob.1973-1985). |
InSfc6h |
Pathname for the 6-hrly surface data and ship data (see ~mesouser/catalog/catalog.sfc, LIST A ). |
InSfc3h |
Pathname for the 3-hrly surface data (see ~mesouser/catalog/catalog.sfc, LIST B ). |
upa_unidate |
8 digit date ( YYMMDDHH ) for upper-air data from Unidata. If more than one time period of data is to be input, upa_unidate may have more than one date. |
sfc_unidate |
8 digit date for surface data from Unidata. Like upa_unidate , sfc_unidate may have more than one date. |
IMX, JMX |
Must be equal to the I and J dimensions of the domain being processed. Must include expansion if the expanded grid is processed. |
LMX |
Must be greater than or equal to the maximum number of levels (mandatory plus new plus surface). |
IRB |
Must be greater than the number of rawinsonde reports which will be processed. |
IRS |
Must be greater than IRB + the number of surface stations which will be processed. |
NNEWPL |
Number of new pressure levels to interpolate to. |
GNLVL |
The pressures at the new levels (bottom to top, mb). |
IWTSCM |
Type of weighting scheme for objective analysis: |
IWIND |
1= Use the surface wind as output from
REGRID for first guess. |
UNIOBS |
T / F: Use Unidata observations (Obsolete. do not touch). |
RWSUBM |
Same as script variable SUBMIT (do not touch). |
IUINTVL |
Time interval of raob data in hours (should be 12). |
ISFCS3 |
T / F: Use 3-hrly surface data (recommended). |
ISFCS6 |
T / F: Use 6-hrly surface and ship data (recommended). |
F4D |
T / F: Create a surface FDDA file. |
INTF4D |
Time interval (hours) for FDDA output (either 3 or 6). |
LAGTEM |
T : Use a 3 hour lag-time for FDDA
first guess. |
NSELIM |
T / F: Specific raobs (Nbogus option) are to be deleted (one flag for each time). Flags refer to 12-hour intervals for non- FDDA jobs; Flags refer to INTF4D intervals for FDDA jobs. |
NBOGUS |
T / F: Nbogus data are included (One flag for each time) Flags refer to 12-hour intervals for non- FDDA jobs; Flags refer to INTF4D intervals for FDDA jobs. |
KBOGUS |
T / F: Kbogus data are included (One flag for each time) Flags refer to 12-hour intervals for non- FDDA jobs; Flags refer to INTF4D intervals for FDDA jobs. |
BUDWGT |
Weighting factor for the BUDDY test. |
ERRMXW |
Maximum difference allowed (m/s) for the ERRMX check for winds. |
ERRMXT |
Maximum difference allowed (K) for the ERRMX check for temperature. |
ERRMXP |
Maximum difference allowed (mb) for the ERRMX check for pressure. |
IPLOT |
T / F: Plot the raobs (One flag for each time period). |
ISKEWT |
Plot the raobs as skew-T (ISKEWT=1) or Stuve (ISKEWT=2) diagrams. |
ISPRINT |
T / F Print surface input observations. |
IFPRNT |
T / F Print out samples of analyses and first-guess. |
1) Obtain the source code tar file from NCAR's ftp site:
ftp://ftp.ucar.edu/mesouser/MM5V3/RAWINS.TAR.gz
2) gunzip the file ("gunzip RAWINS.TAR.gz"), and untar it ("tar -xf RAWINS.TAR"). The directory RAWINS will be created.
3) Go to the RAWINS directory ("cd RAWINS"), create the RAWINS job deck by typing "make rawins.deck".
4) Edit rawins.deck for script options, input data location/file names, parameter statements and namelist values.
5) Make sure you have the required input files: REGRID_DOMAINx, and observations files from NCAR's archive. You may use fetch.job from the Templates/ directory to obtain observations files from NCAR's MSS.
6) Type "rawins.deck >& log" to compile and run the program.
7) Check files "log", and "rawins.print.out" for possible compile and run time errors. If the job is successful, you should at least obtain the RAWINS output file: RAWINS_DOMAINx.
More information can be found in README file in the RAWINS directory.
Always check the printout returned by
RAWINS
. You should check for at least the following:
Various problems may cause
RAWINS
to crash. Careful examination of the printout will often reveal the problem and the solution. Some common problems:
RAWINS reads and writes to and from a number of different files. R AWINS acesses most files by referring to the fortran unit numbers Unit numbers are assigned as follows:
Table 6.1 File names, fortran unit numbers and their description for RAWINS.
In the following example, the following namelist options are assumed:
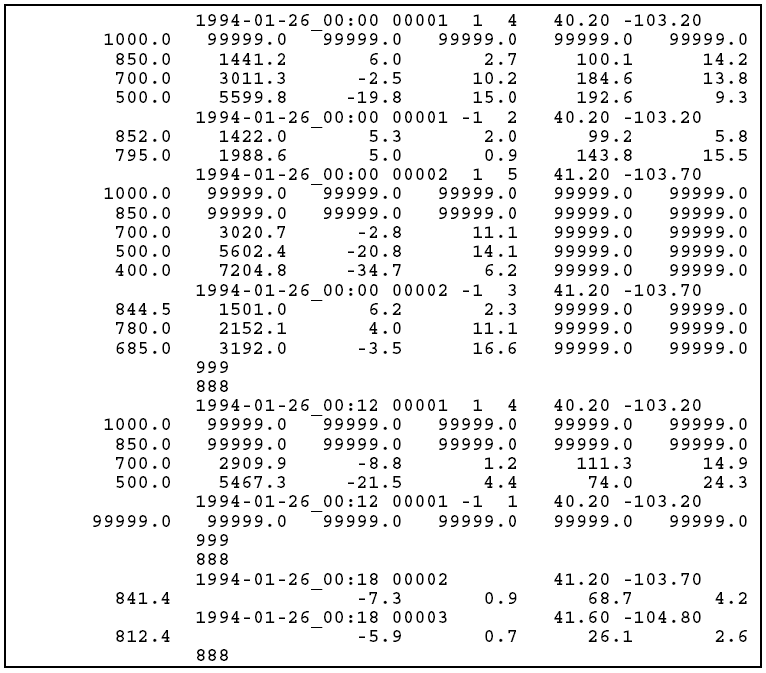
The fields in the station header records are date, station number, integer flag for mandatory (1) or significant (-1) levels, number of levels, latitude, and longitude. The fields in the data records are pressure (mb), height (m), temperature (oC), dewpoint depression (oC), wind direction (degrees from North), wind speed (m s-1).
Note that since Version 3, the date format used in nbogus and kbogus files have been changed to use character*16 format. The format for nbogus file has been changed to
10 FORMAT(22X,A16,1X,A5,2I3,2F8.2)
for upper-air data (mandatory and significant levels), and for surface
The format of KBOGUS data in V3 RAWINS is
40 FORMAT(I4,I2,1X,A8,1X,F7.1,1X,F7.1,4(1X,F7.1),2X,I2,4X,A16)
Note the format for the date has been changed from `I8' to `A16'.