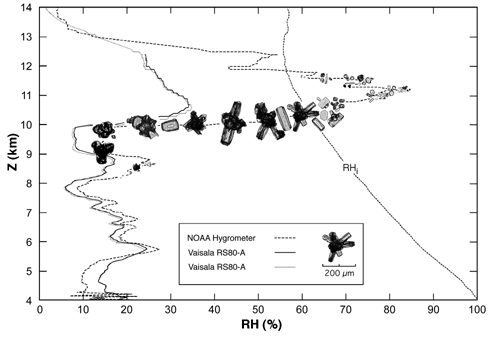

This is an altitude profile of simultaneous relative humidity (RH) measurements from three instruments, with superimposed ice crystals measured by the replicator that represent the ice crystal characteristics through the vertical cloud column, from a multi-instrument balloon launch near Boulder, Colorado. Two RH profiles were measured by Vaisala RS80-A radiosondes, and the RH profile with superimposed ice crystals was measured by the reference-quality NOAA cryogenic frostpoint hygrometer. The variation of ice crystal characteristics in the vertical illustrate a "3-layer model" of cirrus formation and evolution. Layer 1 is the "nucleation layer" near cloudtop, where ice crystals form in ice-supersaturated air. The crystals fall increasingly fast as they grow in the ice-supersaturated air (the "growth layer"), where their mean size increases downward in the cloud and they exhibit pristine and sharp-edged habits (shapes). Below the level of ice-saturation (RHi) is the "sublimation zone", where crystals sublimate and become smaller and more rounded with distance downward in the cloud. Work is in progress to quantify and parameterize the variation in the vertical of cirrus microphysical properties, in order to better represent cirrus in numerical models and remote-sensor retrieval techniques.
Note the poor performance of the radiosonde measurements under conditions of cold temperature and high RH. A correction for these RH measurements has recently been derived in collaboration with researchers at NOAA and Vaisala (Miloshevich et al., submitted to J. Atmos. Oc. Tech.), and work continues on correcting these measurements for the effects of an increasing sensor response-time with decreasing temperature.