MPAS Overview¶
The Model for Prediction Across Scales - Atmosphere (MPAS-A) is a non-hydrostatic atmosphere model that is part of a family of Earth-system component models collectively known as MPAS. All MPAS models have in common their use of centroidal Voronoi tessellations for their horizontal meshes, which has motivated the development of a common software framework that provides a high-level driver program and infrastructure for providing parallel execution, input and output, and other software infrastructure.
Features¶
Important features of MPAS-A include:
Fully-compressible, non-hydrostatic dynamics
Split-explicit Runge-Kutta time integration
Exact conservation of dry-air mass and scalar mass
Positive-definite and monotonic transport options
Generalized terrain-following height coordinate
Support for unstructured variable-resolution (horizontal) mesh integrations for the sphere and Cartesian planes
Support for global and limited-area simulation domains
MPAS-A includes support for the following parameterizations of physical processes.
These are taken from the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) Model.
Radiation: CAM and RRTMG long-wave and short-wave radiation schemes
Land-surface: NOAH land-surface model
Surface-layer: Monin-Obukhov and MYNN
Boundary-layer: YSU and MYNN PBL schemes
Convection: Kain-Fritsch Tiedtke, New Tiedtke, and Grell-Freitas convection parameterizations
Cloud microphysics: WSM6, Kessler, and Thompson schemes
Model Components¶
MPAS-A is comprised of the following two primary components:
- Initialization component
Generates initial conditions for the atmospheric and land-surface state, updates files for sea-surface temperature and sea ice, and lateral boundary conditions
- Model
Includes atmospheric dynamics and physics
Both components are built as cores within the MPAS software framework and make use of the same driver program and software infrastructure. However, each component is compiled as a separate executable.
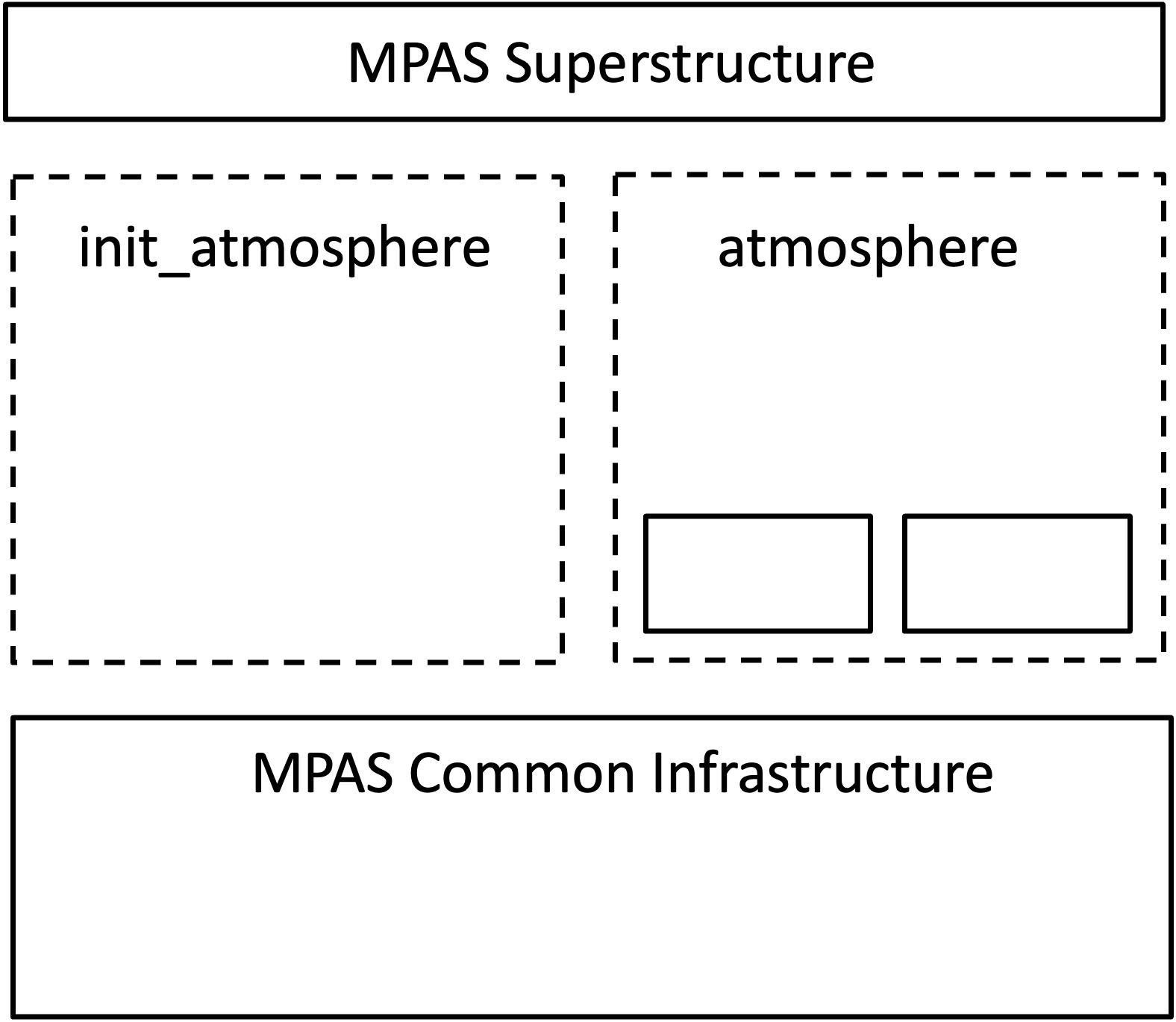
The initialization and model components of MPAS-A are built as separate *cores* within the MPAS framework.¶
See the Quick Start Guide for a succinct description of building and running MPAS-A.
See Building MPAS for detailed instructions for building these components.
See Running MPAS for basic steps to create initial conditions and run the MPAS-A model.
