Model for Prediction Across Scales - Atmosphere¶
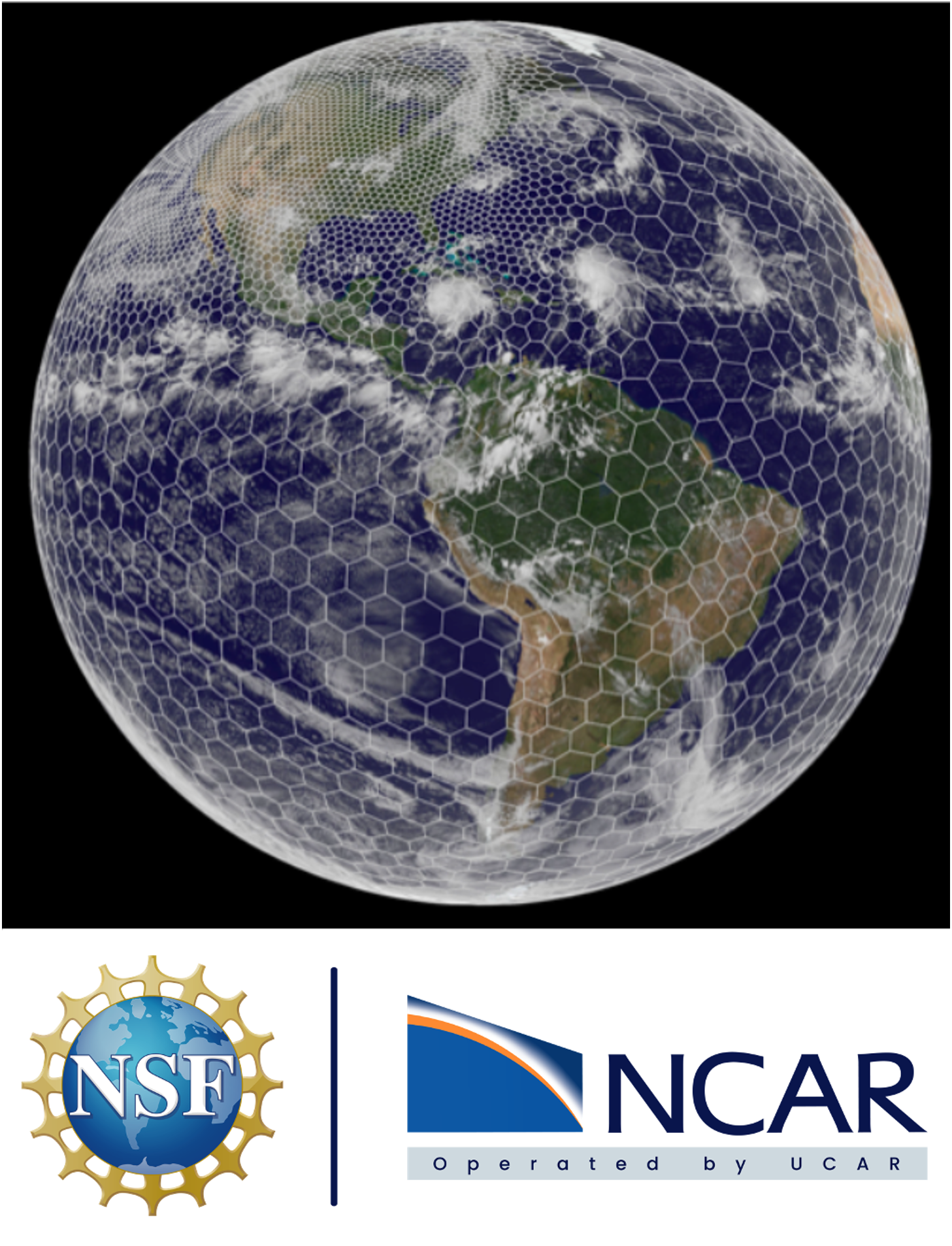
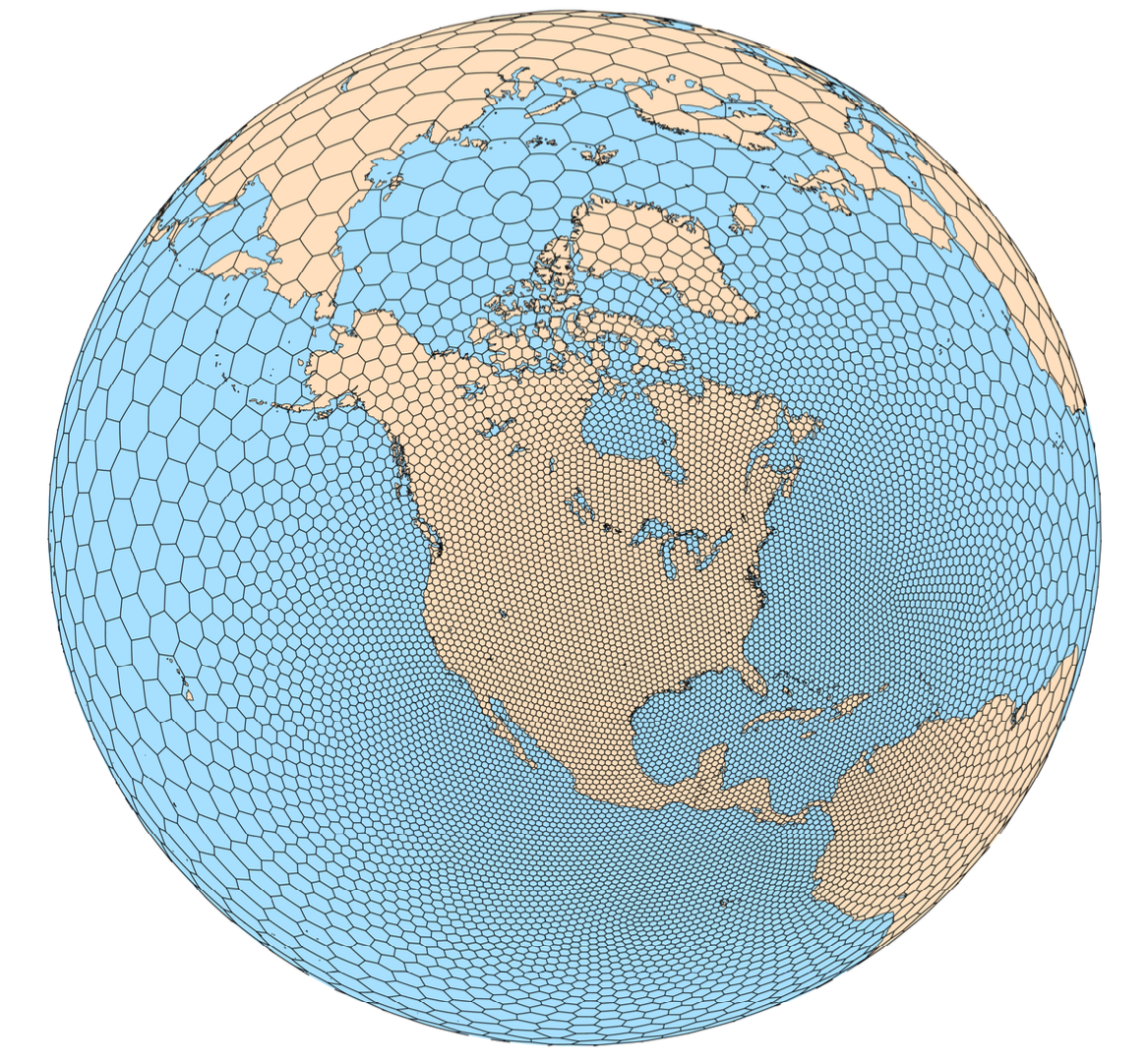
The atmospheric component of MPAS uses an unstructured centroidal Voronoi mesh (grid, or tessellation) and C-grid staggering of the state variables as the basis for the horizontal discretization in the fluid-flow solver. The unstructured variable resolution meshes can be generated having smoothly-varying mesh transitions (see figure (a) below), which ameliorates many issues associated with the traditional mesh refinement strategy of one-way and two-way grid nesting where the transitions are abrupt. The flexibility of the MPAS meshes allows for applications in high-resolution numerical weather prediction (NWP) and regional climate, in addition to global uniform-resolution NWP and climate applications.
Information and links to MPAS-A source code, static geographical datasets, meshes, and input files for real-data and idealized test cases
Documentation specific to GPU-enabled MPAS-A, including important notes, supported platforms, obtaining, compiling, and running GPU-enabled MPAS.
Visualization and Analysis Tools
Example scripts for plotting MPAS-A simulation output
Find announcements and details about MPAS-A Workshops and Tutorials (including a tutorial practice guide)
Access a list of known MPAS-relevant publications, as well as non peer-reviewed presentations
Other Flavors of MPAS
Access other MPAS systems, managed by groups outside of NSF NCAR